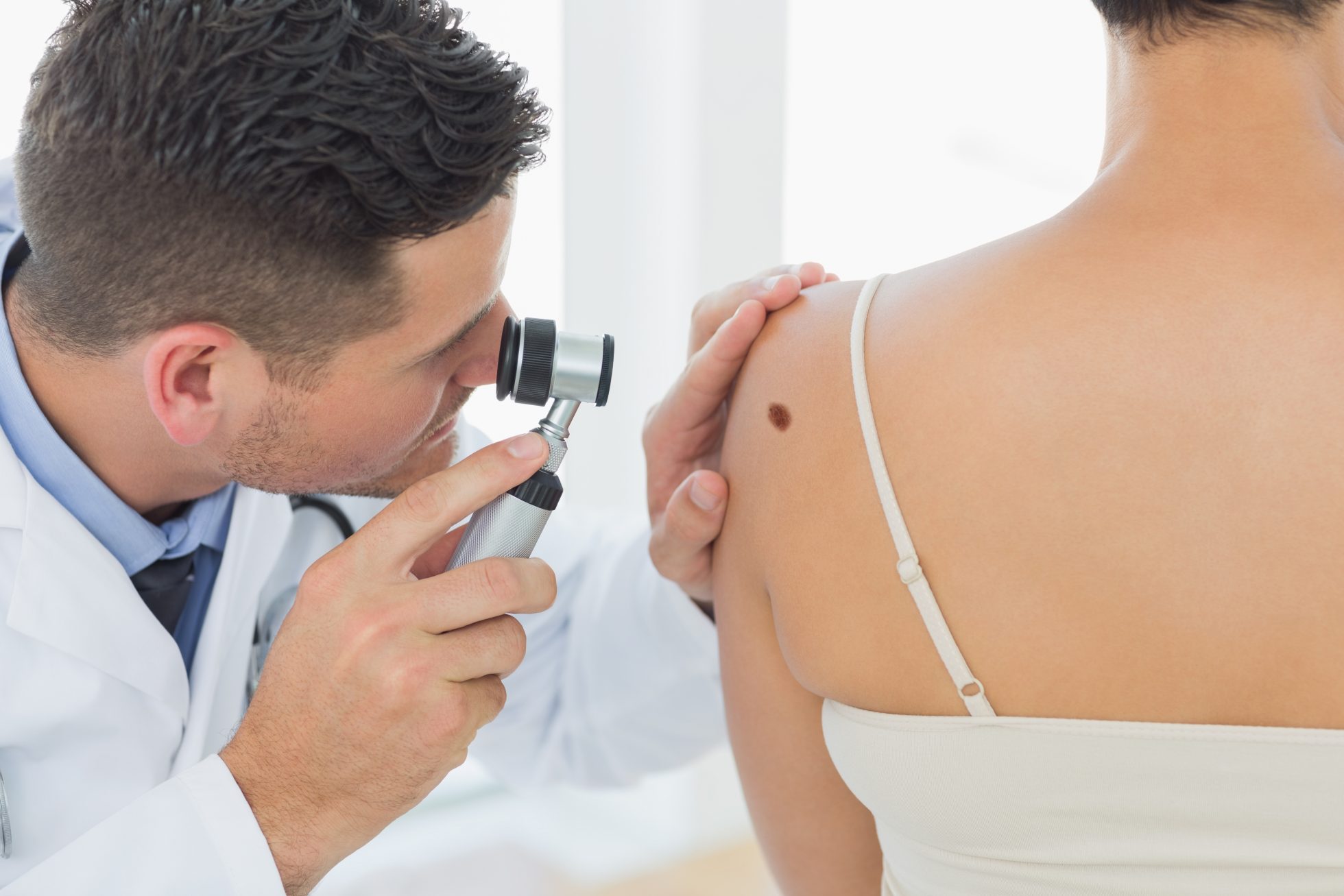
Melanoma treatment
Canada
-
Our Price USD 9234
-
Hospital Price USD 9720
-
You Save : USD 486
Booking Amount: USD 923. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Procedure Description:
Melanoma treatment:
The main course of treatment for melanoma at all stages is surgery to remove the tumor. To remove the melanoma and some of the surrounding normal tissue, a broad local excision is performed. To conceal the surgical wound, skin grafting. the process of using skin from another area of the body to replace the skin that is removed, may be employed.
Disease Overview:
One type of skin cancer that begins in the melanocytes is called melanoma. The cells called melanocytes produce the pigment that gives skin its color. We refer to the pigment as melanin. Usually, melanoma begins on skin that is frequently exposed to sunlight. This covers the skin of the legs, arms, back, and face. Moreover, melanoma can develop in the eyes. In rare instances, it may occur internally, including in the throat or nose.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Not every mole is the same. They might exhibit certain traits that point to melanomas or other skin malignancies. Qualities could consist of:
1- shape that is asymmetrical. Seek out moles that have atypical shapes, such two distinctly different-looking parts.
2- color shifts. Keep an eye out for growths with an odd pattern of colors or multiple hues.
3- shifts in dimensions. If a mole is greater than 1/4 inch (about 6 millimeters), look for fresh growth.
4- alterations in the symptoms. Check for any changes in your symptoms, such any new bleeding or itching.
5- Unusual border. Seek out moles with peculiar scalloped or notched edges.
The appearance of moles that develop into malignancies might vary greatly. While some may exhibit every one of the alterations mentioned above, others might just exhibit one or two peculiar traits.
Disease Causes:
When anything turns healthy melanocytes into cancerous cells, it results in melanoma. Skin cells called melanocytes produce the pigment that gives skin its color. We refer to the pigment as melanin.
What alters the DNA in skin cells and how it results in melanoma is unknown. There's probably a mix of factors at play, including hereditary and environmental ones. Nonetheless, medical experts think that UV light exposure is the main factor that causes melanoma. UV light, commonly known as ultraviolet light, is emitted by tanning beds and lamps as well as by the sun.
The following variables could raise your risk of melanoma:
1. A history of melanoma in the family
2. An earlier sunburn: Melanoma risk may be elevated by one or more severe, blistering sunburns.
3. UV light exposure: UV light, also known as ultraviolet light, is emitted by the sun, tanning booths, and tanning beds. It raises the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers.
4. Relocating to a higher altitude or closer to the equator.
5. Skin prone to sunburn. Melanoma can strike anyone, although white people are more likely to develop it. Melanoma is more prone to occur in those with light-colored eyes, red or blonde hair, freckles, or sunburn easily.
6. Weakened immune system: Melanoma and other skin cancers may be more likely if the body's ability to fight against germs is compromised by drugs or disease.
Disease Diagnosis:
The following tests and techniques are used to detect melanoma:
1. Physical examination: Your physician will inquire about your medical history. In addition, that person will examine your skin for any indications that may indicate melanoma.
2. Extracting a sample of tissue for testing: The process of extracting a sample of tissue for laboratory testing is called a biopsy. The kind of biopsy that is performed depends on your circumstances.
Finding out the cancer's stage—the extent of the disease—is the next step after receiving a melanoma diagnosis. In order to determine the stage of your melanoma, your medical team will:
1. Measure the thickness: A melanoma's thickness is ascertained by measuring it with a specialized tool and examining it under a microscope.
2. Check to see if the melanoma has migrated to the lymph nodes: A sentinel node biopsy may be necessary if there is a chance that the malignancy has spread to adjacent lymph nodes.
3. Search for cancerous lesions outside of the skin. Imaging tests may be done to check for indications of cancer in other parts of the body if there is a fear that the melanoma has spread. MRIs, CT scans, X-rays, and PET scans—positron emission tomography—may be performed as tests.
Disease Treatment:
Surgery to remove the melanoma is typically part of the treatment for melanoma. During the biopsy, a very thin melanoma may be completely excised, in which case no additional care is needed. If not, your surgeon will remove part of the surrounding good tissue in addition to the malignancy.
Patients with thin, tiny melanomas may require simply surgery as a form of treatment. There may be a chance that the cancer has spread if the melanoma has become more deeply embedded in the skin. To ensure that every cancer cell is eliminated, additional therapies are frequently employed.
1. Radiation treatment: Radiation therapy uses intense energy beams to treat cancer. Protons, X-rays, and other sources are possible sources of the energy.
2. Immunotherapy: An medication-assisted cancer treatment, immunotherapy stimulates the body's immune system to destroy cancer cells.
3. Targeted therapy: Medications that target particular molecules in cancer cells are used in targeted therapy. Targeted therapies have the ability to kill cancer cells by preventing these substances from functioning.
4. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses powerful medications to treat cancer. There are numerous chemotherapeutic medications available. Most are administered intravenously. Some are available as pills.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
4 Days
Days in Hotel
*
10 Days
Room Type
Private